Carp PG Collection and Processing Centers: Supporting Sustainable Aquaculture and Fish Reproduction
Carp PG (pituitary gland) collection and processing facilities are critical components of the aquaculture business, notably for carp breeding and reproduction. Carp is one of the world’s most frequently produced fish species, renowned for its flexibility, quick development, and nutritional value. These institutions play an important role in supporting carp populations by providing hatcheries with the resources they need to induce spawning, assuring a steady supply of fingerlings for fish farming enterprises.
The role of carp pituitary glands in reproduction
Carp’s pituitary gland supplies essential reproductive hormones, notably gonadotropins, which promote ovulation and spawning. These hormones are essential for regulated breeding in aquaculture operations, allowing hatcheries to synchronize spawning cycles and increase overall production efficiency. Carp PG injections allow hatchery management to stimulate spawning in a timely way, which is critical for meeting the fish market’s seasonal demands.
Importance of PG in Carp Hatcheries.
The availability of high-quality carp PG is critical to breeding success. Hatcheries may manage the timing and success rate of carp spawning by providing PG injections, resulting in a continuous supply of fingerlings to support fish farming operations. This is especially crucial in areas where fish farming is a major source of revenue and food security. Aquaculture facilities that use controlled breeding cycles can lessen their reliance on wild fish stocks, supporting more sustainable practices and contributing to the protection of natural ecosystems
Commitment to Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Many carp PG collection and processing centers are increasingly focusing on sustainability and environmental responsibility. These centers often implement eco-friendly practices to minimize their impact on the surrounding environment. For example, some facilities use water recycling systems to conserve water resources, while others have adopted waste reduction protocols to decrease the amount of organic waste produced during processing.
By embracing sustainable practices, these centers contribute to the long-term viability of the aquaculture industry. This focus not only helps in conserving natural resources but also ensures that the centers can continue to support the fishing communities that rely on carp farming for their livelihoods.
The Future of Carp PG Collection and Processing.
As worldwide demand for carp grows, PG collecting and processing centers play an increasingly vital role. Innovations in aquaculture technology and hormone processing are constantly enhancing these centers’ efficiency and effectiveness. By investing in research and implementing cutting-edge processes, the sector is working to address the difficulties of rising production while maintaining sustainable practices.
Carp PG collecting and processing facilities are critical to the aquaculture business, ensuring that carp farming remains a dependable and sustainable source of food for millions. These centers’ efforts not only benefit local economies and food security, but also lead the path for more responsible and environmentally sensitive aquaculture methods.
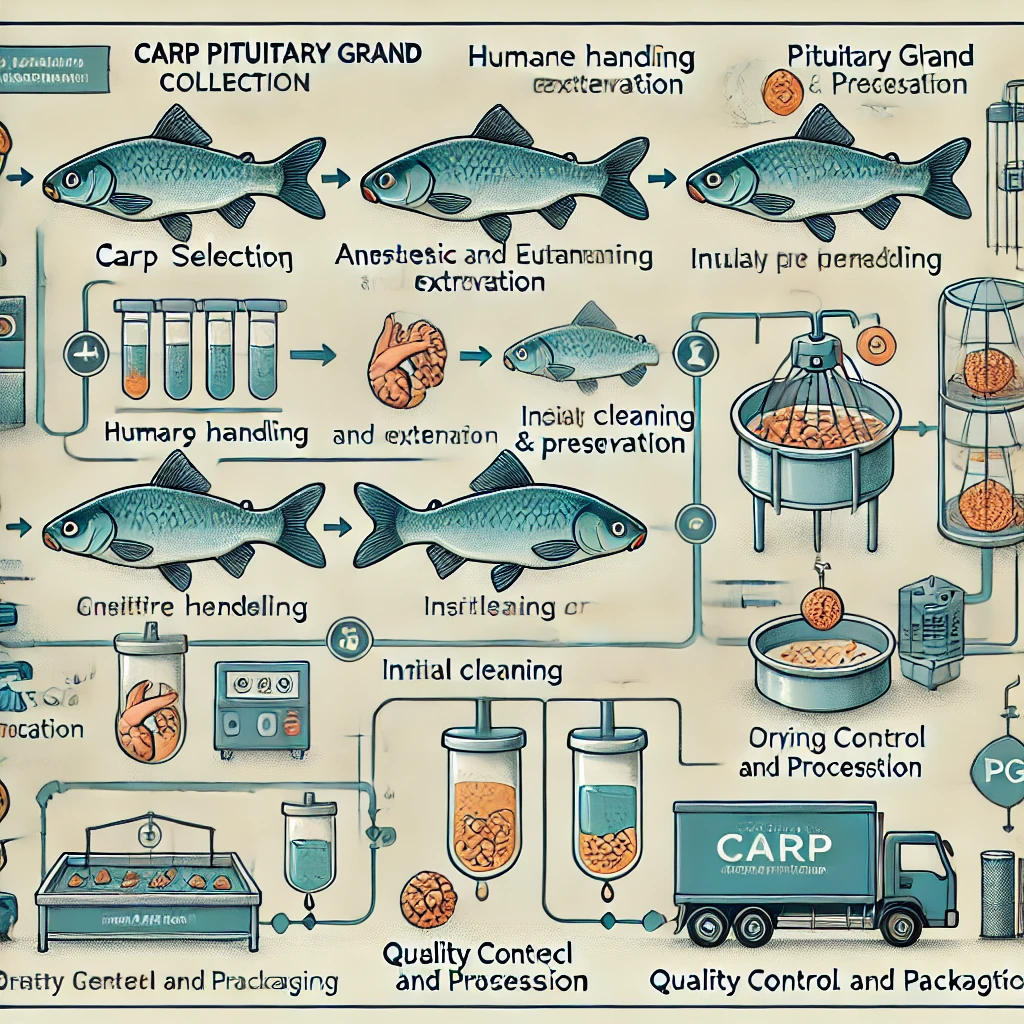
Carp PG Collection Process Flowchart
Carp Selection
- Criteria: Mature, healthy carp with optimal reproductive potential.
- Process: Examination and selection by technicians.
↓
Humane Handling
- Transport and handle carp under humane conditions.
- Minimize stress to maintain fish health and PG quality.
↓
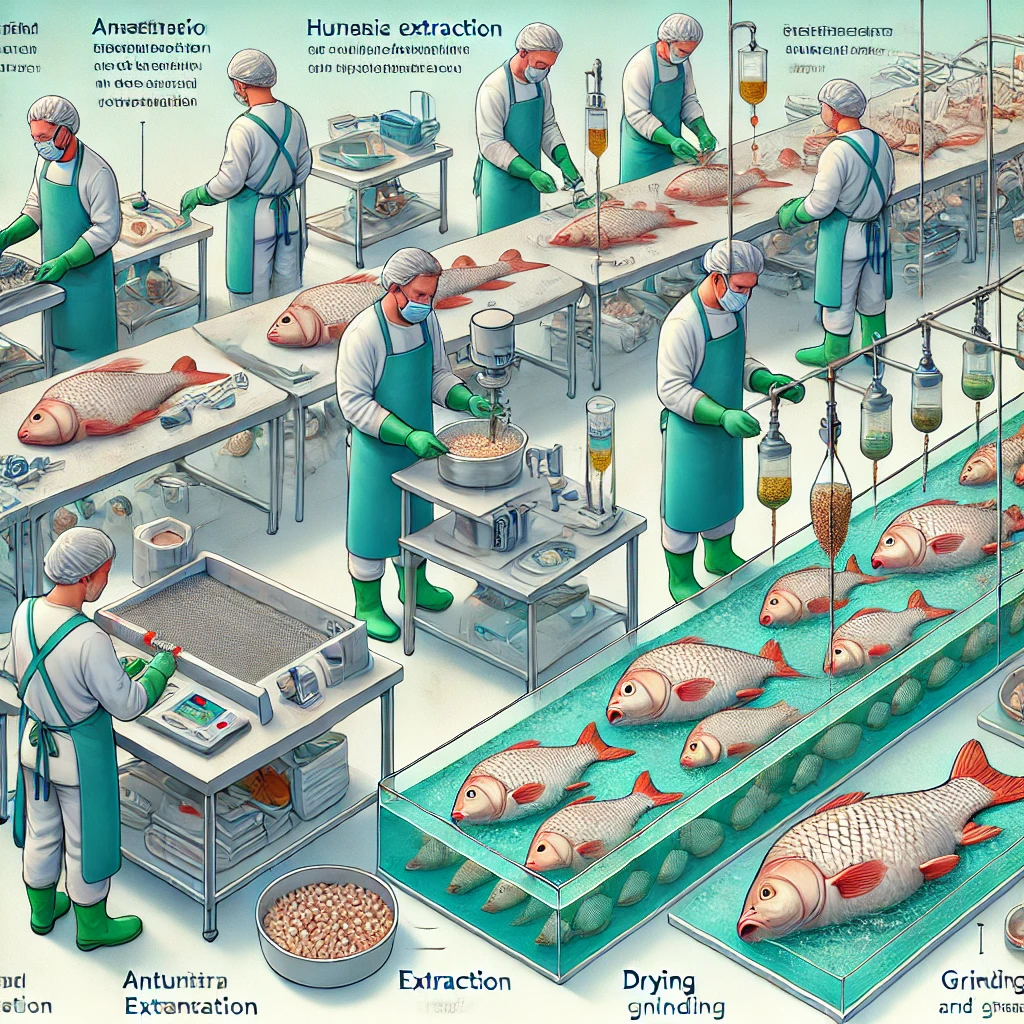
Anesthesia and Euthanasia
- Anesthesia: Apply to minimize discomfort.
- Euthanasia: Humane euthanasia following ethical guidelines.
↓
Pituitary Gland Extraction
- Dissection: Technicians locate and extract the pituitary gland.
- Collection: The gland is carefully removed and preserved.
↓
Initial Cleaning and Preservation
- Cleaning: Remove any excess tissue or contaminants.
- Preservation: Place glands in suitable storage solutions for transport.
↓
Drying and Processing
- Drying: Dehydrate the glands to prepare for grinding.
- Grinding: Grind dried glands into a fine powder for easy handling.
↓
Quality Control and Packaging
- Quality Check: Ensure hormone potency and purity through testing.
- Packaging: Pack processed PG in sealed containers for distribution.
↓
Storage and Distribution
- Storage: Maintain in a cool, dry, and sterile environment.
- Distribution: Supply to hatcheries and aquaculture facilities for breeding use.